

Explore our boiler blog for expert insights, industry updates, and valuable tips on boiler maintenance, efficiency, and more.
Explore our boiler blog for expert insights, industry updates, and valuable tips on boiler maintenance, efficiency, and more.
In every industrial setting, steam boilers deliver essential heat and power. Yet many operators underestimate how critical steam boiler water treatment is to overall efficiency and equipment life. Untreated feedwater can cause scaling, corrosion, foaming and other issues that drive up fuel use, increase downtime and shorten boiler lifespan. This guide explains how a complete boiler water treatment system works, the problems it prevents, and practical steps to maintain an effective program.
A steam boiler water treatment system combines mechanical and chemical processes to remove or control impurities in feedwater before it enters the boiler. Typical components include water softeners, deaerators, filtration units, chemical dosing systems and blowdown equipment. Together they control hardness, dissolved oxygen, pH and total dissolved solids (TDS).
Treatment usually begins with pre-treatment (filtration, softening or reverse osmosis) to remove suspended solids and hardness. Chemical conditioning then stabilizes pH, scavenges oxygen and prevents foaming. Treated feedwater is supplied to the boiler and regular blowdown removes concentrated dissolved solids to keep chemistry within target ranges.
Scale forms when calcium and magnesium precipitate on heat transfer surfaces. Even thin deposits reduce heat transfer efficiency dramatically, forcing the boiler to burn more fuel to reach rated output.
Dissolved oxygen, carbon dioxide and low pH cause corrosion of boiler metal and steam lines. Corrosion leads to leaks, weakened tubing and costly repairs or replacement.
Impurities and high dissolved solids can cause foaming; water droplets are then carried over with steam. Carryover contaminates steam-using equipment (turbines, exchangers) and can cause mechanical damage.
Lack of proper steam boiler water treatment increases fuel consumption and maintenance frequency, while reducing the useful life of the boiler. These hidden costs often exceed the investment in proper treatment.
Softeners remove hardness ions (calcium and magnesium) that form scale. Preventing scale preserves heat transfer efficiency and reduces cleaning downtime.
Deaerators remove dissolved oxygen and carbon dioxide from feedwater, which is critical to preventing corrosion in boiler drums and steam lines.
Chemical dosing injects oxygen scavengers, pH stabilizers, dispersants and anti-foaming agents to keep water chemistry stable and prevent corrosion and deposits.
Filtration removes particulates; RO units reduce dissolved salts and TDS. RO is often required for high-pressure or high-purity steam systems.
Blowdown periodically removes concentrated dissolved solids from the boiler drum, maintaining the required chemical balance and preventing carryover and foaming.
Clean heat transfer surfaces and correct chemistry reduce fuel use. Many plants realize 5–15% fuel savings after implementing or improving a treatment program.
Preventing corrosion and scale extends the life of boiler tubes, drums and ancillary equipment—lowering total cost of ownership.
Fewer unplanned outages and less frequent cleaning or tube replacements cut maintenance labor and spare parts expenses.
Stable water chemistry reduces failure risk (cracking, leaks) and improves overall plant reliability and safety.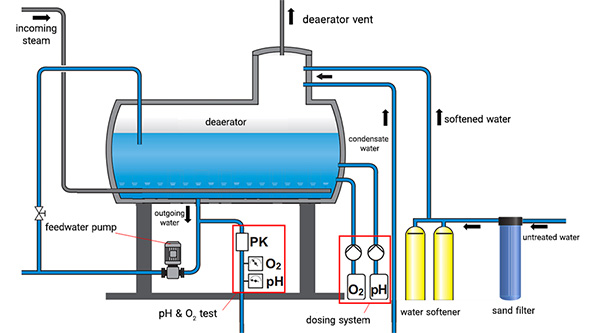
Monitor pH, conductivity, TDS, hardness and dissolved oxygen regularly. Trending these values helps detect issues early and adapt dosing programs.
Inspect softeners, deaerators, chemical pumps and filters on a preventive schedule. Replace consumables (resin, filters, nozzles) before they impair performance.
Select oxygen scavengers, alkalinity builders and dispersants matched to your boiler type, feedwater source and operating pressure. Incorrect chemistry can do more harm than good.
Ensure operators understand water chemistry effects, can read test results and know corrective actions. Trained staff reduce response time to water quality excursions.
Selection depends on feedwater quality, boiler pressure, steam purity requirements and budget. Low-pressure systems may need only softening and chemical dosing; high-pressure plants typically require RO plus advanced chemical control. Work with experienced water treatment vendors to design and commission systems tailored to your needs.
A robust steam boiler water treatment program is not optional—it’s essential. Proper pre-treatment, chemical conditioning and routine maintenance protect heat transfer surfaces, prevent corrosion, and ensure safe reliable operation. Investing in water treatment lowers fuel bills, reduces downtime and extends boiler life. For industrial facilities that rely on steam, clean water equals sustained performance.

We have more than 20 years of experience in boiler system equipment research and development and manufacturing. And committed to designing and producing boilers that suit your needs, including fire-tube, water-tube, and steam boilers, while also staying up-to-date with the latest technological boiler.
Get in touch