

Explore our boiler blog for expert insights, industry updates, and valuable tips on boiler maintenance, efficiency, and more.
Explore our boiler blog for expert insights, industry updates, and valuable tips on boiler maintenance, efficiency, and more.
A practical guide for operators, maintenance teams and procurement — learn how waste oil steam boilers convert used oil into reliable steam, how efficient they are, typical uses, challenges and selection tips.
Waste oil steam boilers burn used petroleum-based oils—such as engine oil, gear oil and hydraulic oil—to generate steam. For facilities that produce or can source significant volumes of waste oil, these boilers turn a disposal liability into an energy asset, reducing fuel bills and waste handling costs while providing industrial steam for heating and process use.
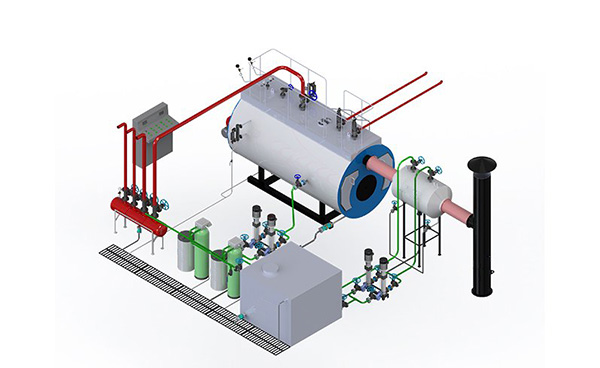
A waste oil steam boiler is an industrial boiler specifically engineered to accept and burn reclaimed oils of varying viscosity and contamination levels. Compared with standard fuel oil boilers, waste oil boilers include dedicated fuel preparation, preheating and atomization systems to ensure stable combustion.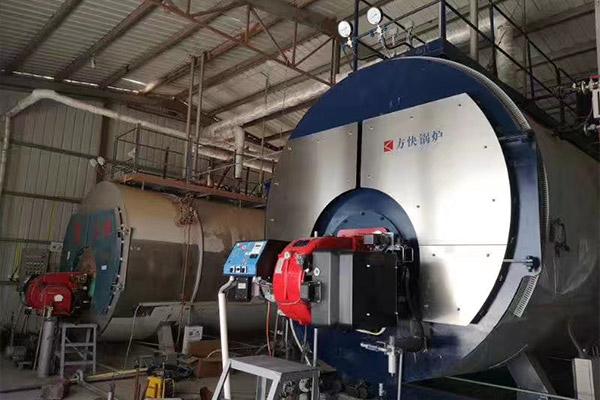
Collected waste oil is filtered to remove metal fragments, sludge and water. Preheating reduces viscosity so the oil can be pumped and atomized reliably.
The preheated oil is sprayed through a specially designed nozzle; fine droplets mix with combustion air and burn inside the furnace. Proper atomization and air–fuel ratio are critical for stable, low-emission combustion.
Hot flue gases pass through the boiler's tubes or heat surfaces, transferring energy to boiler water and producing saturated or superheated steam depending on the design.
Generated steam is routed to process lines, heating systems or sterilization equipment. Condensate is returned to the boiler feedwater system where practical.
Exhaust gases may pass through economizers, air preheaters or particulate control devices (cyclone, baghouse) to recover heat and comply with emission limits.
Modern waste oil boilers typically achieve thermal efficiencies of 80%–90%, depending on burner quality, fuel preparation, boiler design and heat-recovery equipment.
Waste oil must be adequately filtered and free of water and large solids. Improper fuel increases fouling, emissions and maintenance needs.
Burning waste oil can produce particulates, SOx and other pollutants—compliance with local environmental standards is mandatory. Investing in flue-gas cleaning may be required.
Expect more frequent cleaning of burners, heat surfaces and ash handling compared with clean-fuel systems. A solid maintenance program preserves efficiency and safety.
Use certified burners and controls—incorrect combustion of contaminated waste oil can cause flame instability or damage to the boiler.
When selecting a unit, evaluate:
Tip: request detailed fuel-spec tests and combustion tuning reports from suppliers to verify performance with your specific waste oil.
Waste oil steam boilers can offer significant economic and environmental advantages where reliable waste oil supplies are available. With proper fuel preparation, modern burner technology and appropriate emissions controls, these boilers deliver efficient, stable steam for a wide range of industrial applications. Always prioritise compliance, safe design and a robust maintenance plan to maximise benefits and minimise risk.

We have more than 20 years of experience in boiler system equipment research and development and manufacturing. And committed to designing and producing boilers that suit your needs, including fire-tube, water-tube, and steam boilers, while also staying up-to-date with the latest technological boiler.
Get in touch