

Explore our boiler blog for expert insights, industry updates, and valuable tips on boiler maintenance, efficiency, and more.
Explore our boiler blog for expert insights, industry updates, and valuable tips on boiler maintenance, efficiency, and more.
Understanding how a fire tube boiler works is key to selecting the right one for your application. This definitive guide will walk you through everything you need to know, from its design and operation to types, components, and more. Read on to become a fire tube boiler expert!
A fire tube boiler is a simple but versatile design used across various industries. It consists of a steel cylindrical shell containing several horizontal tubes through which hot gases from the combustion chamber flow.
The fire tube boiler definition is straightforward - water surrounds these fire tubes, which are heated by the combustion gases. The heat is transferred from the hot gases to the water via the tube walls, producing steam. The combustion chamber is located at one end of the boiler, while the smokebox is at the other.
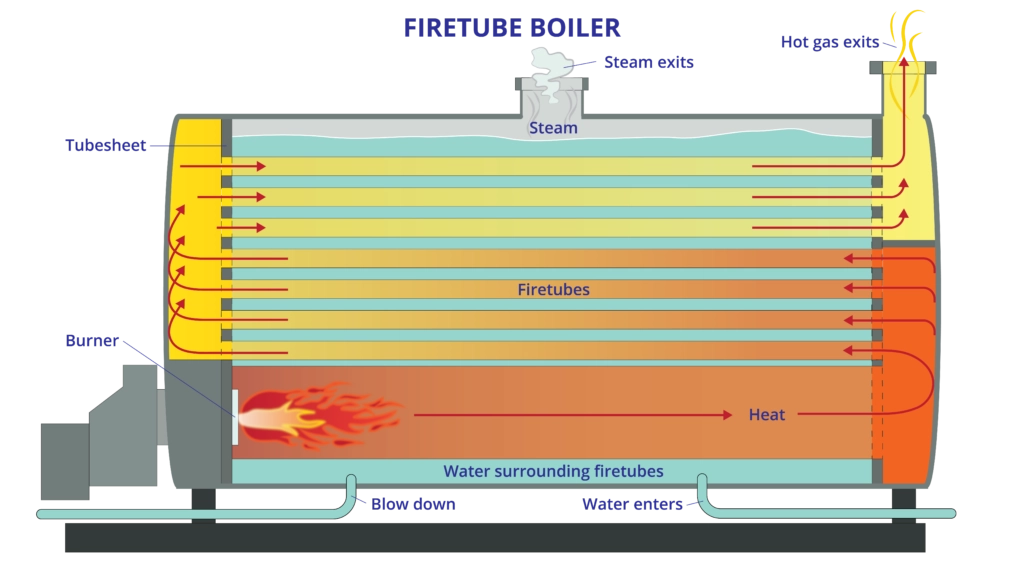
The diagram below illustrates the essential components and working principles. Water enters through the feed check valve, filling the space around the tubes. Fuel is burned in the combustion chamber. Hot gases flow through the pipes, transferring heat to the water and generating saturated steam. This steam rises to the highest point of the boiler, the steam dome, where it is collected before flowing to the engine or turbines.
Fire tube boilers are simple in design and easy to operate and maintain, making them a popular boiler type for steam generation and heating applications.
Now that we know what a fire tube boiler is let’s look at how they operate:
The fire tube boiler operation begins with fuel combustion in the burner. This fuel is generally coal, oil, natural gas, or biomass fed into a combustion chamber at one end of the boiler.
Inside the combustion chamber, the combustion process takes place. A forced draft fan supplies the air required for burning the fuel. As the fuel undergoes combustion, hot gases are generated.
These hot gases then pass through the multiple fire tubes running lengthwise through the boiler. As they move through these tubes, the fire tube boiler heat transfer process happens. The heat from the gases gets through the tube walls, heating the water surrounding them.
The water absorbs the heat and converts it into saturated steam at full boiler pressure. This is the steam generation process. The steam rises to the highest point and collects in the steam drum. It is then taken for use in various applications.
Different types of fire tube boilers are classified based on orientation, tube design, number of tube passes, etc. The main varieties include:
This is one of the most common types of fire tube boilers. As the name suggests, it has a horizontal orientation. The furnace area is at one end, and tubes run longitudinally through the cylindrical shell. These boilers are best suited for low-capacity steam applications.
Vertical fire tube boilers have a smaller footprint and are more space-efficient. They have a vertical cylindrical shell with the furnace at the bottom and tubes going up vertically between tube sheets. This design is often used in mobile boiler applications.
This features a horizontally aligned shell with fire tubes arranged in a radial pattern between front and rear tube sheets. The furnace is located beneath the shell.
The Cornish boiler has a long horizontal cylinder with a single large flue containing the fire grate. It uses a long horizontal flue tube with a relatively low-pressure capacity.
This boiler features two large flues containing fire grates. The enhanced heating surface area allows increased steam generation. Lancashire boilers have various boiler tubes across the flue as well.
It consists of a large cylindrical shell with two fire tubes and flues. The furnace tube diameter is much larger than the shell, giving it higher steam capacities. Scotch boilers are mainly used in marine applications.
This boiler has a horizontally placed cylindrical shell with a combustion chamber beneath. The hot flue gases traverse multiple fire-tubes giving it a high heating surface area. Locomotive boilers are widely used in steam locomotives.
It has vertical fire tubes submerged in water within a cylindrical or rectangular furnace enclosure. The burner fires into the furnace below the tubes. Immersion-fired boilers provide efficient heat transfer.
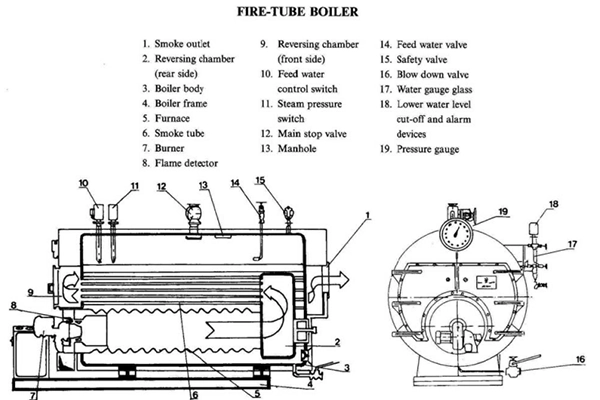
The major components of a typical fire tube boiler are:
While both boiler varieties employ similar working principles, several vital aspects differentiate fire tube and water tube boilers.
The layouts of these boilers are completely opposite. Fire tube boilers have long steel tubes housed within a much larger steel shell filled with water. Hot combustion gases flow inside these tubes. Hence, tubes are surrounded by water.
In contrast, water tube boilers contain numerous narrow water tubes held in a furnace or combustion chamber. Water flows inside the tubes while hot gases envelope around them. This reversed positioning allows better heat absorption into the water for faster steam generation.
Overall efficiency of any boiler determines the effectiveness of fuel utilization. Water tube boilers have greater thermal efficiency levels of 80-85% since water is exposed to hot gases over a larger surface area. This rapid water circulation allows faster heat transfer.
The efficiency of fire tube boilers ranges from 70-80% based on design. But with additional energy saving features like condensers, thermal efficiency can go up to 90%. Fire tube boilers endure stand-by losses which bring down total efficiency.
Operating pressure directly impacts steam generation rates. As water tube boilers can withstand higher internal pressures, their capacity for producing high pressure saturated or superheated steam is significantly greater.
Large utility water tube boilers can generate up to 1,500,000 lb/hr of steam while industrial scale units produce over 10,000 lb/hr. In comparison, the capacity of fire tube boilers max out at 50,000 lb/hr for high end models.
The maximum pressure handled by water tube boilers is between 3000-5000 psi. Extreme pressures well over 1000 psi require expensive alloy steel piping. This allows flexible configuration for power generation or process needs.
On the other hand, fire tube boilers are limited to operational pressures below 300 psi as standard. Custom designs may permit over 350 psi but beyond that, they pose an explosion risk. This narrows their applications.
Purchasing and installing water tube boilers demands major capital investment as the exotic alloys and precision manufacturing hike up prices. Larger units above 500 horsepower that run at supercritical pressures require highly skilled personnel. This drives up operating costs.
In comparison, fire tube boilers are far more wallet-friendly. Their straightforward cylindrical shells allow faster assembly using cheaper materials like steel and iron. Operational costs are also modest with easier controls. Hence they suit commercial spaces with lower steam demands too.
By weighing these critical considerations, an appropriate boiler selection can be made for process or power needs.
| Parameter | Fire Tube Boiler | Water Tube Boiler |
| Design | Tubes surrounded by water in shell | Water surrounded by hot gases in tubes |
| Efficiency | 70-80% | 80-85% |
| Steam Capacity | Up to 50,000 lb/hr | Up to 1,500,000 lb/hr |
| Operating Pressure | < 300 psi | Up to 5000 psi |
| Cost | Low capital cost | High capital cost |
| Maintenance | Frequent maintenance | Less maintenance |
| Applications | Process heating, heating | Large-scale power generation |
| Fuels | Can use a wide variety of solid, liquid, and gaseous fuels | Mostly used with liquid and gaseous fuels |
An appropriate boiler can be chosen for specific application requirements by understanding the advantages and limitations.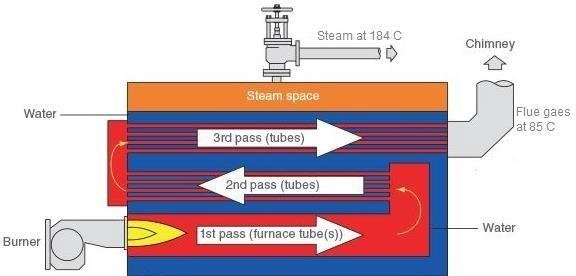
Fire tube boilers find usage across various sectors:
Proper maintenance is crucial for the safety and efficiency of fire tube boilers. Here are some key maintenance tasks:
There are several renowned fire tube boiler manufacturers:
With so many fire tube boiler varieties available, what are the best options? Here are 5 of the top fire tube boilers used across industries:
Due to their compact footprint, vertical fire tube boilers take up minimal floor space. Hot gases pass through the vertical cylindrical shell encasing the firetubes. Though less efficient, these boilers are easy to install and service. Vertical designs are a popular residential heating boiler choice.
Packaged boilers arrive fully assembled and tested by the manufacturer. This simplifies installation and allows quick startup. Packaged fire tube boilers feature multi-pass tube arrangements in an enclosed casing. They offer high efficiency and consistent performance.
These boilers allow the use of renewable fuels like biomass, wood, and agricultural waste. The solid fuel is manually fed into the furnace. Solid fuel-fired boilers are exceptionally environmentally friendly. However, they need special design considerations for handling ash buildup.
The Scotch marine boiler is a highly efficient three-pass boiler. Hot gases pass through the cylindrical shell three times, maximizing heat transfer. Though more expensive, these compact boilers are commonly used in marine applications. Their ability to withstand shock and vibration makes them well-suited for ships.
HRT boilers are a two-pass design with gases flowing through the shell twice before exhausting. This makes them slightly less efficient and more affordable than Scotch boilers. HRT boilers offer reliable steam generation for industrial processes. Their horizontal orientation saves space.
Considering key aspects like efficiency, maintenance, footprint, and fuel source will help narrow down the ideal fire tube boiler choice from these top options.
This comprehensive guide covers everything you need about fire tube boilers, from working principles and configuration to types, pros and cons, maintenance, and applications.
Equipped with this knowledge, you can select the perfect boiler for your specific needs. Reach out to manufacturers for quotes and clarify any additional queries. A quality fire tube boiler system will provide reliable performance for years.

We have more than 20 years of experience in boiler system equipment research and development and manufacturing. And committed to designing and producing boilers that suit your needs, including fire-tube, water-tube, and steam boilers, while also staying up-to-date with the latest technological boiler.
Get in touch